Microsoft Office Outlook 2000 Advanced Setup Guide
Recently, we have been hearing more reports of people having many diffrent problems configuring and setting up their email accounts using varying range of email clients. This guide will be one of a series of guides which aims to help you through the process of configuring your email client to receive emails from your email account. Additionally, it will also show you additional useful settings and features which may help enhance your experience when using these email clients.
Today, we will be looking at the email client which seems to be causing users the most problems, Microsoft Outlook. The version I will be using is Microsoft Office Outlook 2000, which is an older version. If you wish to view a guide for an up-to-date version of Microsoft Outlook, please check out the Outlook 2010 guide in this blog.
This guide is aimed at advanced users with an greater understanding of computing, if you wish to view a beginner setup guide, please look at this guide.
Microsoft Office Outlook 2000
Setup
For most users, the process of connecting your email account to the email client should be fairly straightforward. Upon first loading the client, you will be presented with a setup wizard, as shown in the screenshot below. From here you will be able to configure this email client to connect to the email account that you wish to connect to.
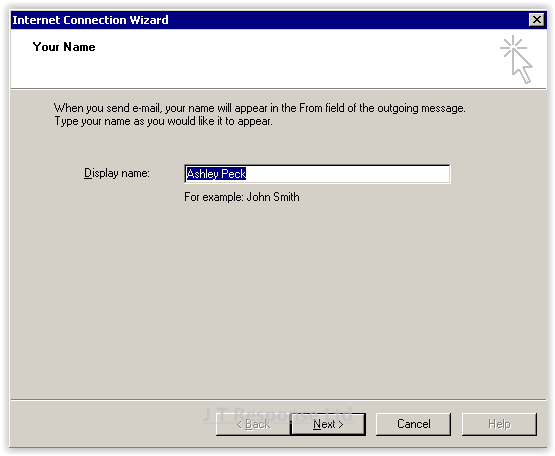
This window prompts you to enter a display name to be associated with the email account you are connecting to.
- Display Name: This is the name you wish to be displayed alongside your email address in any emails that you send. This is also the name which recipients will see when they receive an email from you.
Once you have completed entering this piece of information, press Next to continue progressing through the setup wizard.
Automatic Email Account Setup
In Microsoft Outlook 2000, there is no option to automatically configure and connect to email accounts. Due to this, I will be unable to provide a guide for automatic setup. Please refer to the Manual Email Account Setup section of this guide to learn how to connect to your email account using this email client.
Manual Email Account Setup
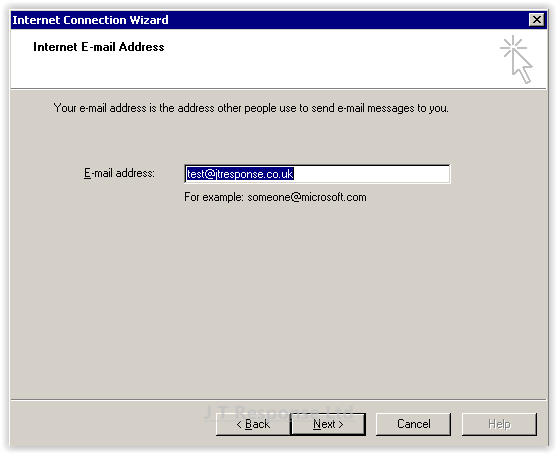
The next screen will prompt you to enter the email address of the email account you wish to connect to using this email client.
- E-mail Address: This is the email address which you wish to connect to using this email client.
Once you have completed entering this piece of information, press Next to continue progressing through the setup wizard.
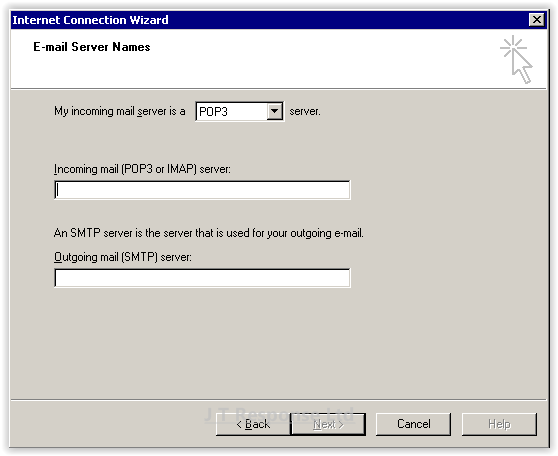
The next screen will prompt you to enter several pieces of information relating to the email server you wish to connect to. All of these details should be provided to you by your email host.
- Protocol: The protocol is selected at the top of the window by the dropdown included inside of the phrase, My incoming mail server is a ___ server. Here you can select what type of protocol the incoming mail server uses. The options here are either POP3 or IMAP.
- Incoming mail server: This is the address of the incoming mail server for your email server. This information should be provided by your email host.
- Outgoing mail server: This is the address of the outgoing mail server for your email server. This information should be provided by your email host.
Once you have filled out these fields, press Next to continue progressing through the setup wizard.
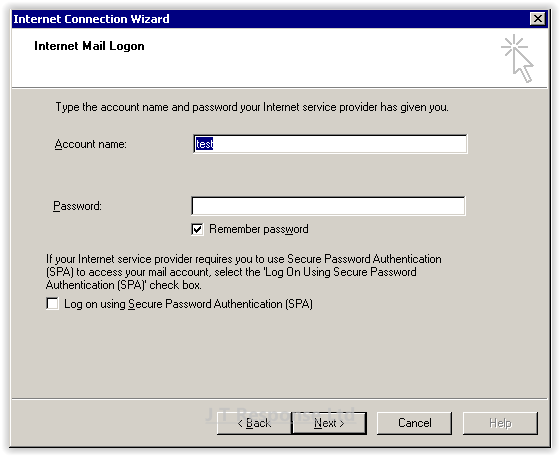
You will now be prompted to provide your log in information for your email account. These details are what will be used to connect to your email account on the email server which was entered on the previous screen. These screen requires several pieces of information.
- Account Name: This is the user name which you will be using to try to connect to your email account on the email server you specified. Typically, this would be the same as the user name which you would use to connect to your email account.
- Password: This is the password which you will be using to try to connect to your email account on the email server you specified. Typically, this would be the same as the password which you would use to connect to your email account.
- Log on using Secure Password Authentication (SPA): This specifies whether to use Secure Password Authentication (SPA) when trying to connect to your email account. If your email server requires you to log on using this method of authentication, ensure that this checkbox is checked.
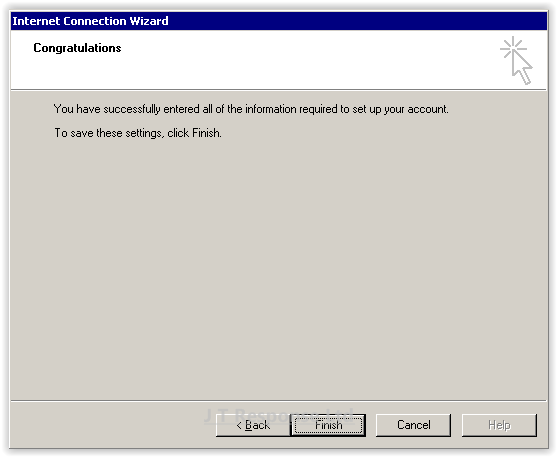
Once you have completed this information, press Next.
Your email client should now be correctly configured to connect to your email account. If you have any issues connecting to your account, please ensure that all the details which you have entered are correct. If the problem still persists, contact your email host for further assistance.
Features
Now that you have your email account configured with Microsoft Outlook 2000, there are several features which may prove helpful during your time using this email client.
Create Rule
One feature which we will be looking at will be Rules. Rules are used to tell Outlook to perform a particular action when certain conditions are met. An example of such a rule is to forward specified emails to an email address when they are received by the email client. Rules can help expand and automate what the email client does and can help tailor your email client to suit your needs.
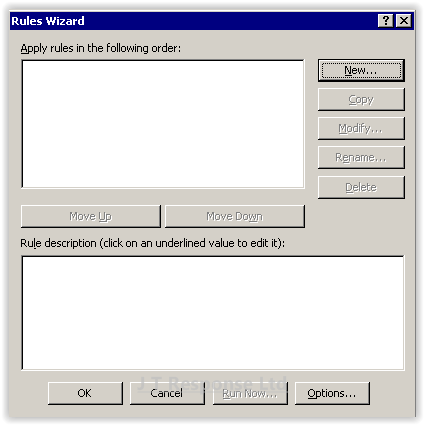
The first step to creating a rule is by pressing the Tools button on the menu bar and then selecting the Rules Wizard option.
This will bring up the window as shown in the screenshot above. This window will display a list of all the rules which are currently associated with your email account. In order to create a new rule, we must press the New button. If we wish to modify or delete existing rules, we can press the Modify and Delete buttons respectively.
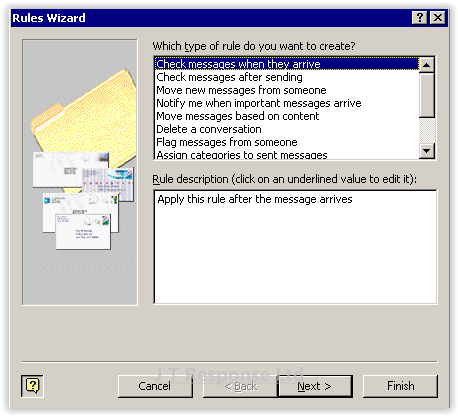
By pressing the New button, the following window will be displayed. This window contains options to create the conditions of a rule. The conditions of a rule are the WHEN part of the rule, specifying when a rule should be carried out. The top box in this window allows us to select the type of condition which we wish to use in our rule. The second box is used to further specify this condition. We can add additional conditions in the next screen, however all of the conditions for a rule must fall under the same category, unlike more modern email clients.
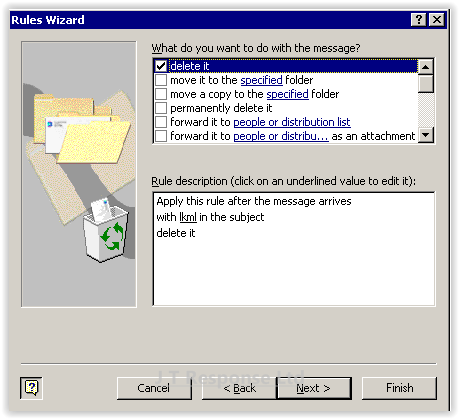
The next screen is where we can specify what action the rule will carry out when the conditions are met. The actions of a rule are the WHAT part of the rule, specifying what the rule should do when a message meets all of the conditions. Once again, the top box is used to specify the type of action which is to be taken. The bottom box is used to further specify the action. Once you have selected all of the actions you wish to carry out and have further configured them in the bottom box, press the Next button.
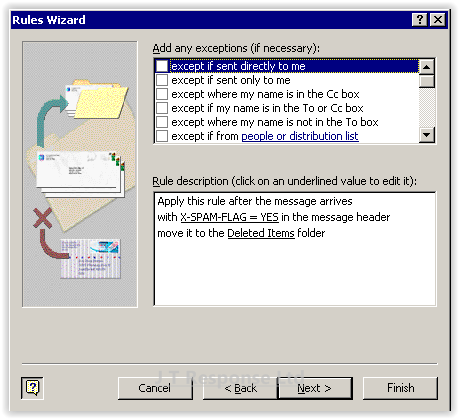
The next screen is used to specify exceptions to the rule. Exceptions are used to tell the rule to ignore messages which meet the conditions set in this screen. An example of this is to ignore all messages received from a certain email address. This can be used to add yet more customisation and control to your rule. Once you have finished adding exceptions, press the Next button.
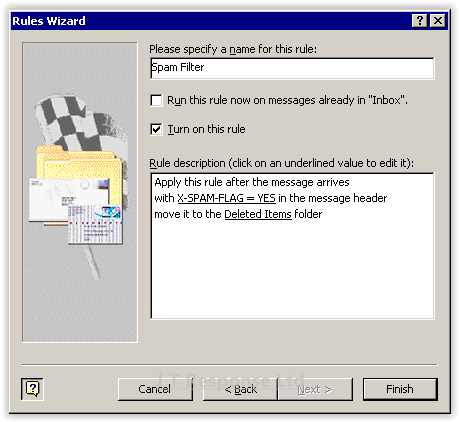
This final screen will allow you to assign a relevant name to your rule, as well as giving you a summary of all of the features of your rule which you have selected. In addition to these pieces of information there are two checkboxes.
- Run this rule now on messages already in “Inbox”: This will run your rule against emails which you have already received and are in your inbox. Any messages which meet the conditions will have the appropriate action taken against them, unless they meet the exception criteria.
- Turn on this rule: This will specify whether the rule will become active when you finish the Rules wizard.
Once you are happy with your rule, press the Finish button to finish the creation of your rule.
Spam Rule Example
In this example, I will be showing you how to create a rule which will automatically deal with any spam received by your email client. The way we will be doing this is by looking into the email headers received with the message. The email header contains all the necessary information required to ensure that your email is routed to the correct email server and account, as well as providing vital information such as who the email was from. In addition to these details, the anti-spam methods put in place by the email server will add additional lines in the header to score email messages in an attempt to prevent spam. These headers are what we will be looking at in this example.
In our email server, spam is given a score based on various factors. If the spam score for a given message is greater than 6, it will be flagged as spam and appropriate actions can be taken by the email client.
To create our rule we will once again go to Tools in the menu bar and select the Rules Wizard option. In this window, we will then select New to create a new rule. This will bring up the create rule window where we will be creating our rule.
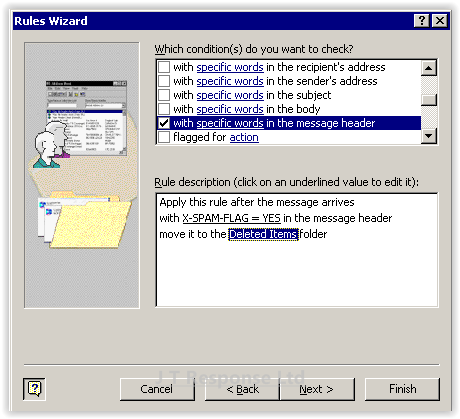
As we are looking to filter emails which meet the spam condition, we must look at the email header for each email that we receive. To do this, the with specific words in the message header option must be checked. By going down to the box below the condition list, we can specify what we are looking for in the header for the condition. With our email server, there are several ways of doing this. We can either search for emails containing the spam flag with values of YES or for a more specialised filter, we can search for emails with specific spam scores to be filtered. You can add as may phrases to be searched for in the header as you like so your spam filter can be as complicated as you wish.
The header we will be looking for is X-Spam-Flag. If a message has a spam score which is greater than 6, then this value will be equal to YES, else the value will be equal to NO. In this case we wish to catch all the messages which are marked as YES, so we will search the message header for the line X-Spam-Flag = YES. We will now press Next to move to the next step in the rule creation process.
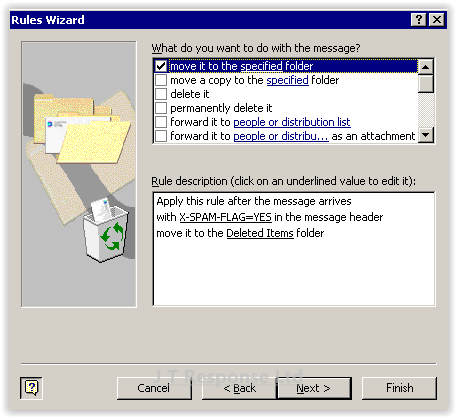
The next step is to specify what to do with the spam emails we have flagged. In this example, we wish to automatically move the spam email to our Deleted Items folder. To do this we must check the option to move it to the specified folder and then in the bottom box, specify that we wish to move it to the Deleted Items folder. We will now press Next to advance in the rule creation wizard.
Finally, we can choose to add exceptions to our rule. In this example, I will not be choosing to add any exceptions to the rule. However, exceptions can be used to stop certain messaged from going to the Deleted Items folder, even if they meet the spam criteria. An example of when this could be useful is if you wanted to ensure that all emails coming from a certain email address will never be marked as spam, even if they meet the criteria. We will now press Next to advance through the wizard.
This is the final screen in the rule creation process. We can now name and save our rule and turn it on to catch any spam it receives. We will call our rule Spam Filter as these seems like an appropriate name to call a rule of this type. We can now press Finish after ensuring that Turn on this rule has been checked to enable our rule.
Troubleshooting
Relay Access Denied
To resolve this issue, please follow the following steps.
Press the ‘Accounts’ option under the ‘Tools’ menu.
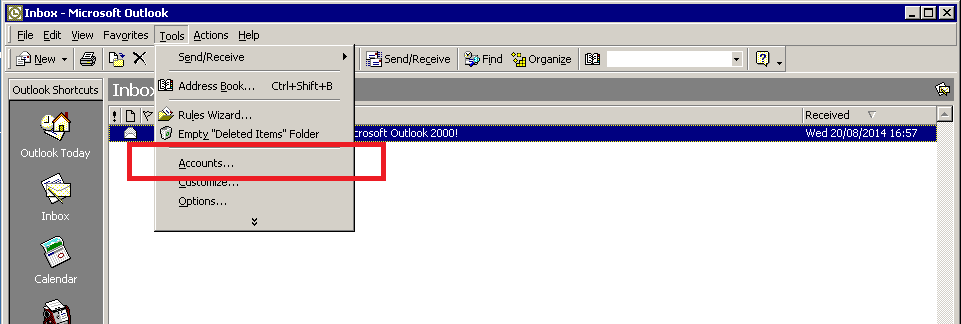
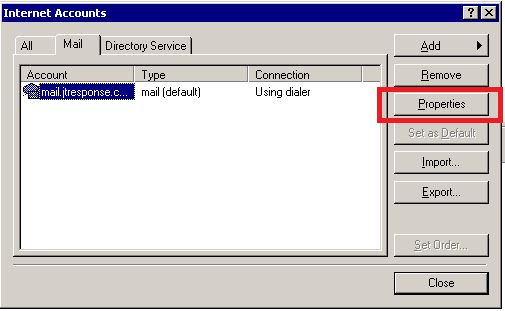
Select your email account and press the ‘Properties’ button on the right.
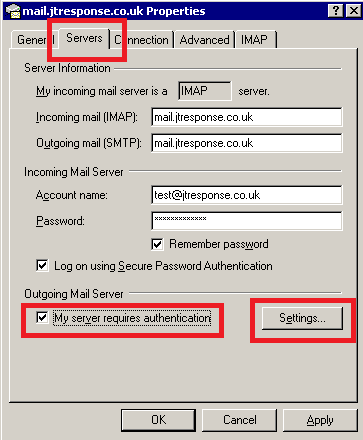
Navigate to the ‘Servers’ tab. Ensure that the ‘My server requires authentication’ checkbox is checked. Press the ‘Settings’ button.
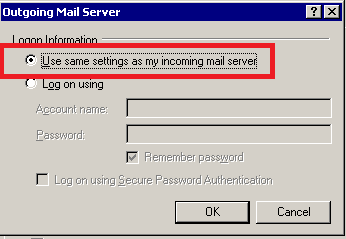
Ensure that the ‘Use same settings as my incoming mail server’ option is selected. Press OK to save your changes.
This issue should now be resolved.
Summary
I hope that this guide will help you to setup, configure and use Microsoft Outlook 2000. Guides may become available in the future for other versions of Microsoft Outlook, however I believe that most of the steps in this guide should be similar to the steps required in these versions. If you have any questions about this guide, please comment below and I will be happy to assist you.